

This blog serves as an essential guide to the Request for Quotation (RFQ) process, which is crucial for effective vendor selection in business procurement. We shed light on what is Request for Quotation and its significance for businesses and provide a comprehensive request for quotation template. We will also explore different RFQ types, the distinction between RFQ and RFP, and the appropriate scenarios for employing an RFQ. It’s a detailed roadmap for businesses to streamline their vendor selection process, emphasizing strategic decision-making and efficient procurement practices.
Making informed decisions about vendor selection has become more crucial than ever. The Request for Quotation (RFQ) is a strategic tool guiding businesses through the labyrinth of vendor options to pinpoint the perfect fit. It’s not just about finding a supplier; it’s about forging partnerships that align with business objectives and drive success.
Imagine standing at a crossroads with various paths leading to potential vendors. In this scenario, an RFQ is your map, offering clear directions and criteria to evaluate each route. It’s more than just cost; it’s a quest for value, quality, and alignment with your project goals. This blog is crafted to take you through this journey, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to confidently navigate the RFQ process, ensuring your business decisions are both strategic and sound.
An RFQ is a formal document a business sends to potential suppliers, inviting them to submit detailed price quotations for specific products or services. It’s akin to a casting call in the world of procurement, where businesses seek the most fitting vendor to fulfill their particular needs.
An RFQ typically encompasses detailed descriptions of the products or services required, allowing suppliers to provide accurate and competitive pricing. It’s not a mere inquiry; it’s a precise request tailored to garner specific information vital for decision-making. The RFQ zeroes in on the cost aspect of procurement, often including aspects like quantity, quality, and delivery timelines.
The RFQ process is a critical step in ensuring efficient procurement for businesses. It provides a structured approach to sourcing, enabling them to streamline the vendor selection process. By issuing an RFQ, businesses can gather essential data quickly and efficiently, allowing them to make informed decisions with clarity and confidence.
Understanding how Requests for Quotation (RFQ) works is vital to grasping their role in business procurement. An RFQ is a streamlined method businesses use to invite vendors to bid on specific products or services, focusing on obtaining the best possible price and terms. Here’s a breakdown of how RFQs function in the business context:
A Request for Quotation (RFQ) is not a one-size-fits-all document. Different types of RFQs cater to various procurement needs, each with its unique approach and use scenarios. Let’s explore these different types.
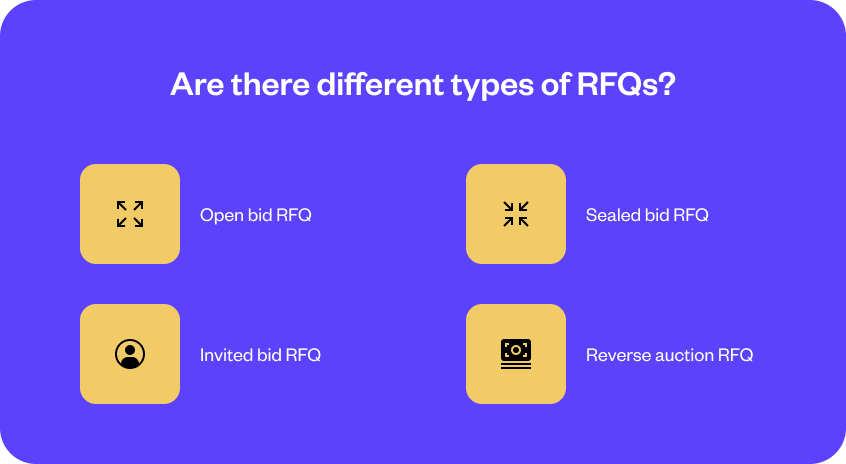
Open bid RFQs are like an open market where any vendor can throw their hat in the ring. Here, the Request for Quotations is made public, inviting many suppliers to participate. This openness creates a competitive atmosphere where vendors can see each other’s bids. It’s akin to an auction where everyone knows the current highest bid, sometimes leading to vendors quoting higher prices to outbid competitors. Open bid RFQs are particularly useful when transparency is crucial and a business seeks to cast a wide net to explore all possible options.
The Sealed bid RFQ operates under a cloak of confidentiality. In this approach, suppliers submit their bids sealed, and these are opened only after the submission deadline. Often favored in government or public sector procurement, this method ensures fairness and impartiality. The sealed bids are a guard against undue influence and help maintain a level playing field, as suppliers bid without knowledge of their competitors’ prices. It’s ideal for scenarios where unbiased pricing and objective vendor evaluation are essential.
The Invited bid RFQ is more exclusive and selective. It’s like being on a guest list where only certain vendors, often those with a prior relationship with the business or those pre-vetted, are invited to submit their quotations. This method can streamline the procurement process, as it involves suppliers known for their reliability and quality. However, this exclusivity may sometimes limit the potential for competitive pricing, as the pool of bidders is restricted.
In a Reverse auction RFQ, the usual bidding dynamics are flipped. Here, vendors compete by offering lower prices rather than bidding up. It’s a race to the bottom in terms of pricing, where suppliers try to undercut each other to win the contract. This type of RFQ is beneficial when the price is the paramount criterion, and the product or service specifications are standard. It encourages vendors to offer their best prices. However, businesses must be vigilant to ensure this fierce competition doesn’t compromise quality or service standards.
A Request for Quotation (RFQ) and a Request for Proposal (RFP) might sound similar, but they’re used for different purposes. Think of it like this: when a business needs to know the price of something specific, it sends out an RFQ. It’s all about getting those numbers. But when things get a bit more complex, like when they’re not just buying a product but might need a whole service or solution, that’s where an RFP comes in. It’s more detailed and asks vendors to propose a way to solve a problem, not just tell the price. So, depending on what a business needs, they’ll pick between an RFQ and an RFP. Let’s understand it through a simple breakdown that explains the main differences, helping you make the right call when dealing with vendors.
| Aspect | RFQ (Request for Quotation) | RFP (Request for Proposal) |
| Primary focus | Primarily focused on the price for specified goods or services | Focuses on comprehensive solutions to a project, including methodologies, innovation, and overall approach, in addition to pricing |
| Nature of project | Suitable for standard, routine purchases where specifications are precise and the requirement is price-driven | Employed for complex, unique projects requiring strategic considerations, technical expertise, and customization |
| Evaluation criteria | Decisions are based mainly on price and the supplier’s ability to meet specified requirements. | It involves a holistic evaluation of vendors, including experience, project approach, technical capability, and alignment with project objectives. |
| Response type | Responses are uniform, focusing mainly on pricing and delivery terms. | Responses vary widely, providing detailed insights into proposed solutions, methodologies, and vendor’s vision for the project. |
| Usage scenarios | It is used when the business knows exactly what it needs in terms of product or service specifications. | It is used when a project’s requirements aren’t just about price but also involve quality, innovation, and strategic alignment with business goals. |
| Decision basis | Decision-making is predominantly price-centric. | Decision-making is based on a variety of factors. It is not limited to cost and includes the vendor’s overall capability to execute the project successfully |
Choosing the right procurement method can be as crucial as selecting the right vendor. A Request for Quotation (RFQ) is not a universal solution but a specific tool best suited for certain scenarios. So, when is an RFQ the ideal choice?
An RFQ, emphasizing cost and specifics, is a pragmatic approach to procurement when the requirements are clear-cut, and the primary goal is to secure the best price.
The RFQ process is a meticulous journey from identifying a need to finalizing a deal. Here’s a breakdown of this process:
The journey begins with in-depth preparation. Define your needs in detail, considering the product or service specifications, quantities, and desired quality. Collaborate with relevant stakeholders within your business to ensure all requirements are captured.
Once your needs are clearly defined, draft and issue the RFQ. Choose your potential suppliers judiciously – whether it’s an open call to the market or a selection of preferred vendors.
As responses come in, it’s time for analysis. This phase involves reviewing the quotes against your specified criteria. Remember, it’s not always about the lowest price. Consider factors like vendor reliability, delivery timelines, and service quality.
Upon selecting a vendor, negotiate if necessary to fine-tune details like pricing adjustments, delivery schedules, or specific terms and conditions.
Finalize the deal with a formal agreement or purchase order. Ensure that all the terms discussed are clearly laid out in the contract. With the contract signed, the implementation phase begins – whether it’s the delivery of products or the commencement of services.
Post-implementation, evaluate the vendor’s performance. Were the products or services delivered as per the agreed-upon standards? Was the vendor responsive and efficient? This evaluation forms a critical feedback loop for future RFQ processes.
Completing an RFQ (Request for Quotation) is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and clear communication. Here’s how businesses typically navigate these steps:
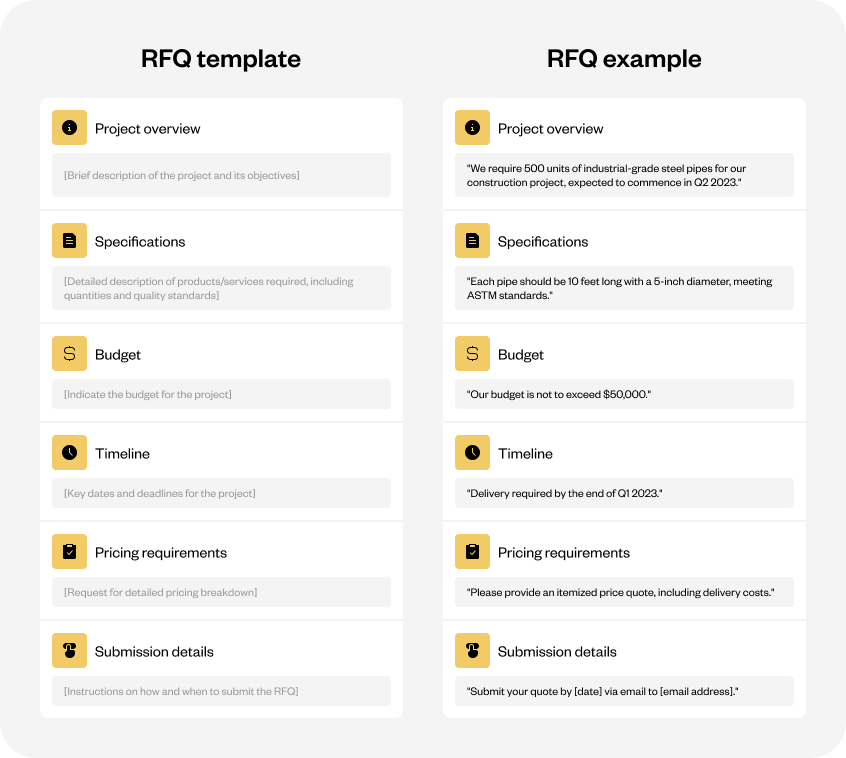
A well-structured RFQ template can significantly streamline the vendor selection process. Below is a sample RFQ template that businesses can adapt to their needs:
Responding to an RFQ effectively can increase your chances of winning the contract. Here’s how businesses should approach an RFQ response:
Understanding and effectively utilizing the Request for Quotation (RFQ) process is a strategic asset. The RFQ, more than a tool for price comparison, stands as a beacon for strategic procurement, ensuring businesses secure the best deals and cultivate valuable supplier relationships. As we conclude, remember that mastering the RFQ process is an ongoing learning curve pivotal in steering your business toward successful and sustainable procurement strategies.
A request for a quote (RFQ) is a procurement document businesses use to invite suppliers to bid for specific products or services, primarily focusing on price. It outlines detailed requirements, such as quantities and specifications, enabling suppliers to offer precise quotations.
Writing an RFQ involves detailing your project requirements, including specifications, quantities, and quality standards. It must outline your budget, desired timeline, and specific instructions for suppliers to submit their quotes, ensuring clarity and facilitating easy comparison of responses.
The main difference lies in their purpose and scope. An RFQ focuses on obtaining price quotes for specific, well-defined items or services. In contrast, an RFP (Request for Proposal) seeks comprehensive solutions for more complex projects, considering factors beyond just price, such as methodology, innovation, and strategic fit.
Typically, an RFQ precedes an RFP when the price is the primary concern, and the requirements are well-defined. An RFP is generally issued first for more complex projects where broader solutions are needed.
To submit an RFQ, businesses distribute the document to selected suppliers, which can be done via email or through a procurement platform. The RFQ should include clear submission guidelines and a deadline, ensuring suppliers understand how and when to respond.
The RFQ response process involves suppliers reviewing the RFQ, assessing their ability to meet the requirements, and then submitting their quotes. These responses should detail pricing, delivery schedules, and any other relevant terms, allowing businesses to evaluate and compare them effectively.
The quotation process involves preparing a detailed RFQ and issuing it to potential suppliers. It follows by receiving and reviewing their quotes, negotiating terms with the selected supplier, finalizing the contract, and then evaluating the supplier’s performance post-contract to inform future procurement decisions.

Biddwan Ahmed is currently leading the NLP team, overseeing research and engineering efforts. Biddwan is responsible for spearheading cutting-edge LLM experiments in the field of artificial intelligence. With a focus on generative AI, Biddwan is driving initiatives to create more meaningful conversational experiences for users. With a strong background in AI, Biddwan continues to drive innovation and contribute to the advancement of the industry.
Biddwan Ahmed is currently leading the NLP team, overseeing research and engineering efforts. Biddwan is responsible for spearheading cutting-edge LLM experiments in the field of artificial intelligence. With a focus on generative AI, Bi. Learn More
Subscribe to Newsletter